Methodology for Electricity Price Forecasting Used in ARE S.A.
The Energy Market Agency S.A. uses a methodology commonly applied worldwide in systemic research for its analytical and forecasting work. We draw on years of experience and collaboration with institutions such as the International Atomic Energy Agency in Vienna (Austria), Argonne National Laboratory in Chicago (USA), and the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis in Laxenburg (Austria). We also possess an extensive database of statistical data that allows us to reflect most key aspects of the functioning of the energy market in Poland in the models we use. The statistical data that underpin ARE S.A.'s models cover the entire supply chain of fuels and energy, including cost and environmental issues.
The Energy Market Agency S.A. has developed a high standard of market information on energy to continually inform its clients about key aspects of energy market operations, enabling them to make informed decisions. We conduct daily analyses of price volatility in the natural gas and electricity markets, analyze the factors shaping the prices of these energy carriers, and assess the legal and market aspects influencing prices. We continuously monitor legislative actions by European Union bodies, initiatives taken by the Polish government regarding the country's energy policy, and opinions from energy sector representatives. Our team comprises experienced analysts specializing in energy statistics, market analysis, and forecasting. We also collaborate with the largest energy companies whose actions determine market operations.
The overall outline of the computational procedure used in ARE S.A. for analyzing the development of the fuel and energy sector and forecasting electricity prices is presented in Figure 1. The calculation results are the outcome of many iterations carried out throughout the entire computational procedure.
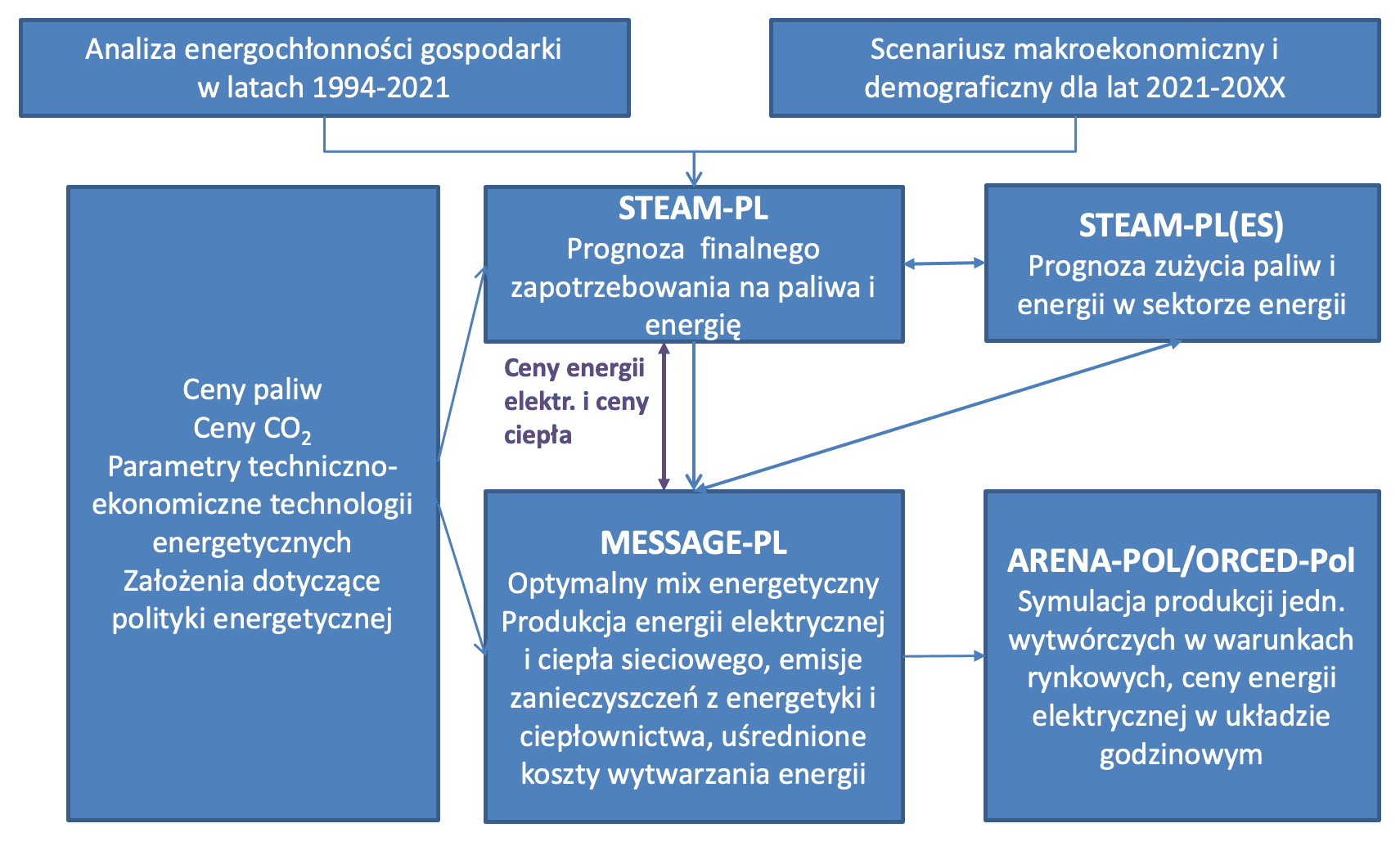
Figure 1. Scheme of the computational procedure and models in forecasting electricity prices at ARE S.A.
When determining future electricity prices, the starting point is to establish the level of electricity demand in the forecast perspective. These figures determine the level of electricity production and available capacity necessary to meet the demand. According to the methodology applied at ARE S.A., the main factors influencing the growth rate of electricity demand include: economic growth, measured by a series of macroeconomic indicators (GDP and value added in various sectors of the national economy), demographic processes, changes in societal lifestyles, technological advancements, and improvements in energy efficiency.
Projections of electricity demand are prepared using the STEAM-PL model (Set of Tools for Energy Demand Analysis and Modeling). This tool was developed at ARE S.A. between 2012 and 2016. STEAM-PL is an "end-use" consumption model dedicated to the national fuel and energy system, accurately reflecting the technical aspects associated with energy use in various sectors of the economy (industry, services, households, transportation, and agriculture). It is an integrated hybrid model that allows for simultaneous determination of future levels of useful energy demand (a "bottom-up" approach) and the ways to meet it (a "top-down" approach). The model is based on a computational algorithm that simulates the behaviors of energy consumers responding to changes in the price relationships of fuels and technology costs (allowing for the analysis of technological substitutions and energy carriers based on costs associated with delivering specific energy services). For this purpose, the model uses econometric modeling of market shares in the form of logit functions (market share algorithm - a mathematical approach used in models such as BALANCE and WEM). This solution allows for a detailed analysis of strategic variables related to pricing policy, such as tax policy concerning specific types of fuel or technology, subsidization of certain solutions in energy use, or the analysis of the impact of price changes resulting from raw material market conditions. The projections generated using the STEAM-PL model (broken down by sectors of the national economy) are constructed based on a single coherent scenario that includes macroeconomic assumptions, demographic assumptions, expected rates of improvement in energy use efficiency, and technological progress.
The results of the STEAM-PL model serve as input data for the MESSAGE-PL model (Model for Energy Supply Strategy Alternatives and their General Environmental Impacts), which determines the optimal generation structure and the required production from individual generating units based on the received electricity and district heating demand. The selection of the optimal generation structure (energy mix) in the MESSAGE-PL model is based on minimizing the total discounted system costs over the entire examined time period. MESSAGE utilizes linear programming methods or, for certain tasks, integer programming methods (e.g., the selection of aggregates with specific capacities - large coal and nuclear units). MESSAGE operates on a user-defined energy flow network (Figure 2), starting from the extraction or supply of primary energy, through transformations (e.g., electricity and heat generation), transmission, and distribution, to end users in industry, agriculture, transportation, services, and households.
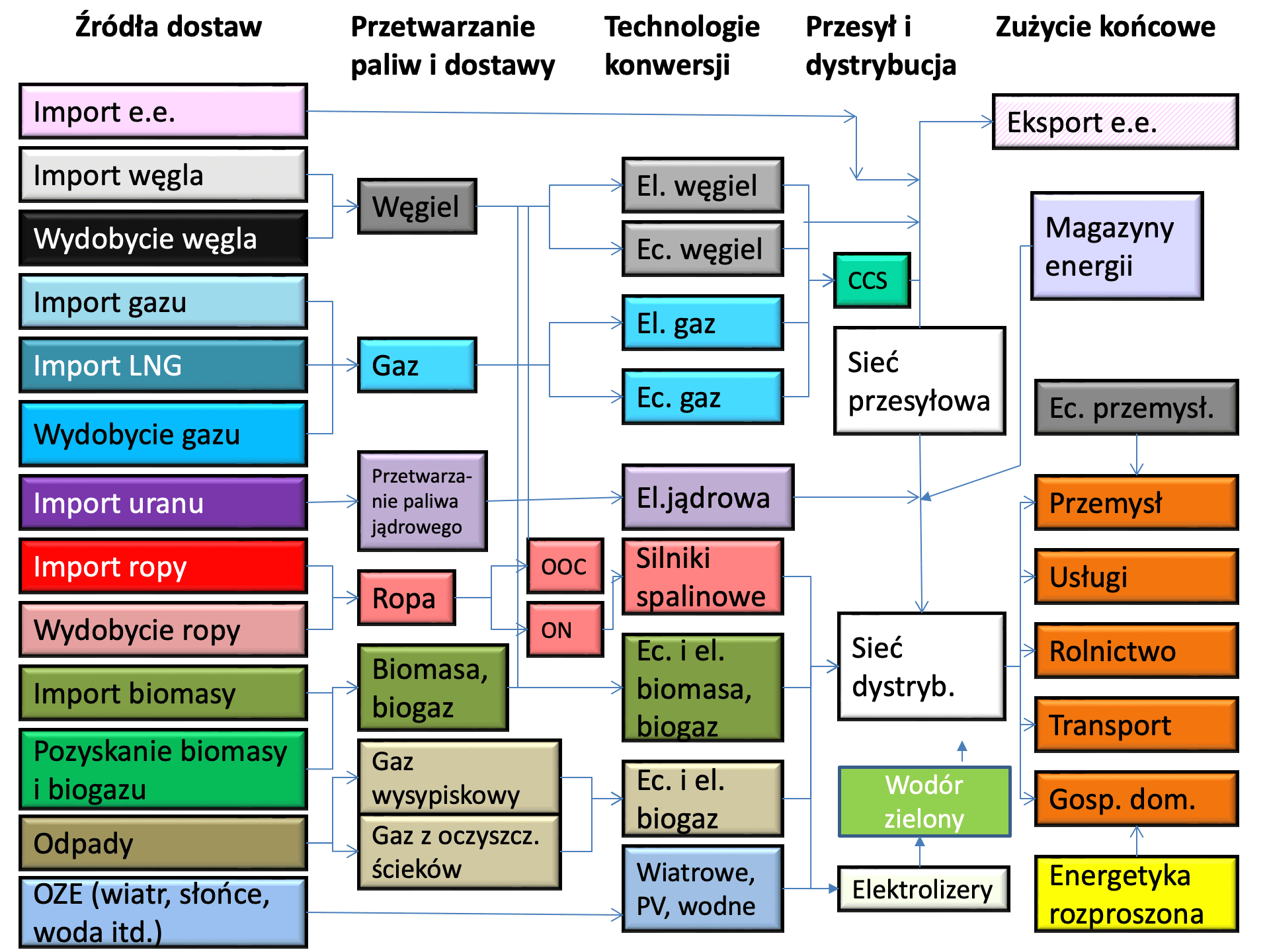
Figure 2. Simplified scheme of the energy system in the MESSAGE-PL model
Both existing technologies and new generating units are part of the network. Currently, the model includes over 80 existing generating units and new types of technologies (including high-efficiency coal and gas technologies with and without CO2 capture, renewable energy sources - RES, nuclear power plants, cogeneration technologies, hydrogen technologies, DSR services, and energy storage). The model considers long-term goals regarding air pollutant emissions and CO2 emissions (including restrictions on emission permits arising from the European Emissions Trading System) and state policy instruments promoting RES and combined heat and power generation.
Based on the energy mix determined in the MESSAGE-PL model for Poland, the next step involves using simulation methods to develop projections of market electricity prices in the wholesale market – in the ARENA-POL and ORCED-PL models. The projections pertain to SPOT prices in the Day-Ahead Market (TGeBase index). They are determined considering the differences in marginal cost levels of system units depending on the load band.
ARENA-POL is a mathematical model comprising a set of interconnected modules used to simulate the electricity market, broken down into hourly data for a long-term perspective (currently until 2050). The model consists of a demand part (Demand_module), a supply part (Supply_module), and a part reflecting cross-border trade (Cross-border trade). The input data for the model includes results from the STEAM-PL models concerning the forecast of electricity demand in the country (hourly curve, accounting for the development of e-mobility, air conditioning, and electrification of industry and heating), MESSAGE-PL – national energy mix, and macroeconomic data such as CPI, exchange rates, fuel prices, certificate prices, planned shutdowns of generating units, network restrictions, and others. The model simulates the operation of generating units in market conditions, broken down into individual blocks (about 80 blocks in JWCD and aggregated units in professional, industrial, and independent combined heat and power plants, RES sources (including distributed), hydropower plants, ESP, DSR services, and energy storage (batteries, hydrogen-based). Electricity price forecasting occurs by determining the marginal cost of generation in a given time interval (for 8760 hours in each considered year) based on a "stack" of generating units arranged from cheapest to most expensive (merit order) according to the offered price (generally the variable costs of electricity generation). The "marginal" unit sets the price for all units lower in the order. Variable costs are determined based on the technical-economic parameters of individual generating units and anticipated production fuel costs, transportation, environmental costs, and other variable costs. Additionally, the model takes into account the level of available capacity reserves in the KSE at a given hour and its impact on electricity price levels – the "scarcity pricing mechanism." The model also simulates cross-border electricity trade by including the availability of transmission capacities on cross-border connections.
The ORCED-PL model, used to determine electricity prices in the Day-Ahead Market (TGeBase index), utilizes historical data and projections from the ARENA-POL model. It implements a stochastic simulation that enables the assessment of price volatility levels in the market while ensuring compliance with historical market price trends. This tool is instrumental in assessing the effectiveness of energy policy instruments, particularly in the context of price expectations and potential risks in energy markets. Both the ARENA-POL and ORCED-PL models are designed to capture complex market dynamics, ensuring a robust framework for electricity price forecasting that is responsive to changing market conditions.
[1] Stanton W. Hadly, The Oak Ridge Competitive Electricity Dispatch (ORCED) Model, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, October 1999.
